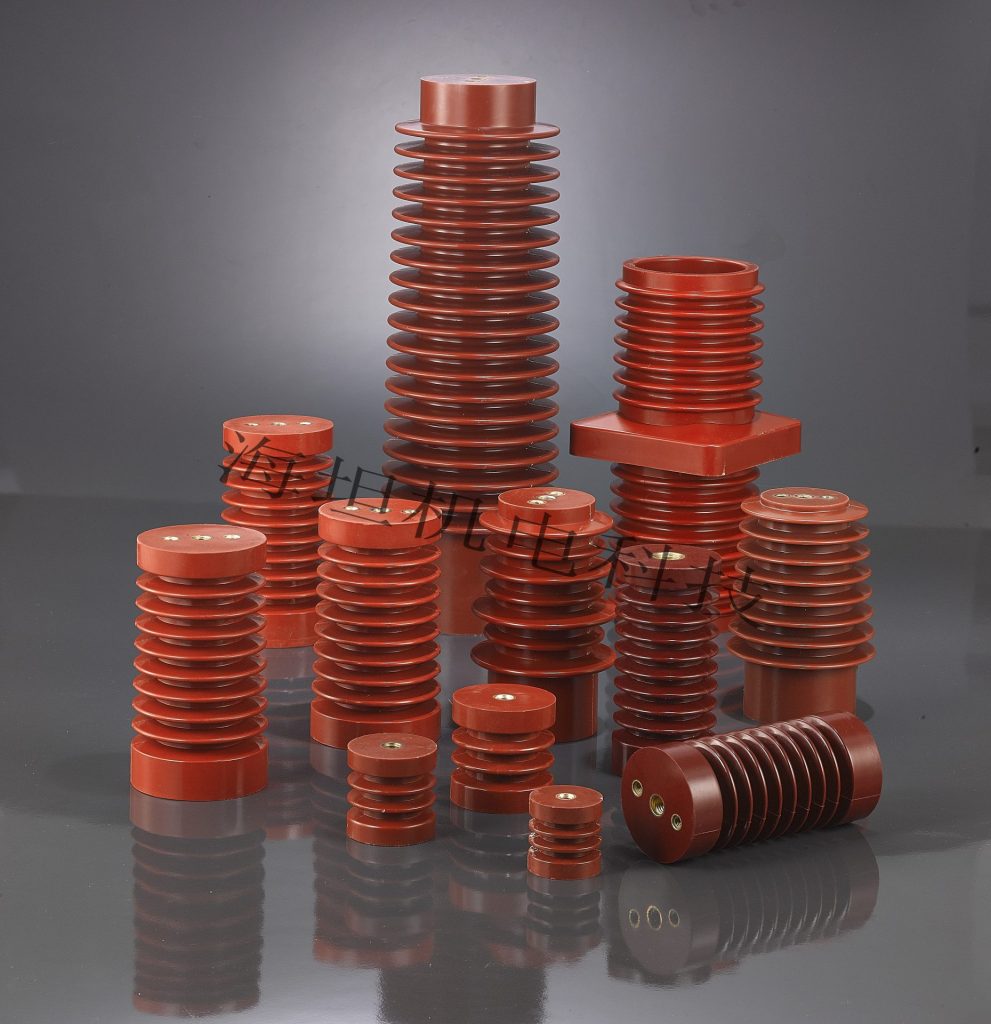
Category
- Busbar Support
For the bus bar frame option, first confirm the specification of your own copper bar. After confirmation, confirm how many phases your bus bar frame is, how many copper bars in total, and what is the phase to phase distance between each phase copper bar and another phase copper bar. Select the type according to the size you need. The common spacing is 55, 80, 100, 110, 120, 130, 140, 150, 160, 175 and 180 (unit: mm). The number of phases includes single phase, three-phase, four phase and five phase. The copper bars that can be installed in each phase are divided into single row, double row, three row and four row.There is also the size of the mounting screw hole of the busbar clamp.
- Heat Shrink Tube
- High Voltage Insulator
- Low Voltage Insulator
What Is Busbar?
A busbar is a metal bar or conductor used for power distribution, usually made of copper or aluminum. It plays a vital role in electrical systems by providing a reliable and efficient means of distributing power from the source to different devices and loads. Busbars are usually designed to carry high currents and have excellent conductivity and heat resistance to ensure stable operation even under high loads.
Busbars are widely used in substations, switchboards, and electric vehicle charging stations. They can be customized to meet specific needs, for example by adding insulation or using special coatings to enhance protection. In addition, bus bar systems are usually modularized for easy installation and maintenance, improving the reliability and efficiency of the entire power system. The use of busbars not only improves the stability of power transmission, but also effectively reduces energy loss, making them an indispensable component of modern power systems.
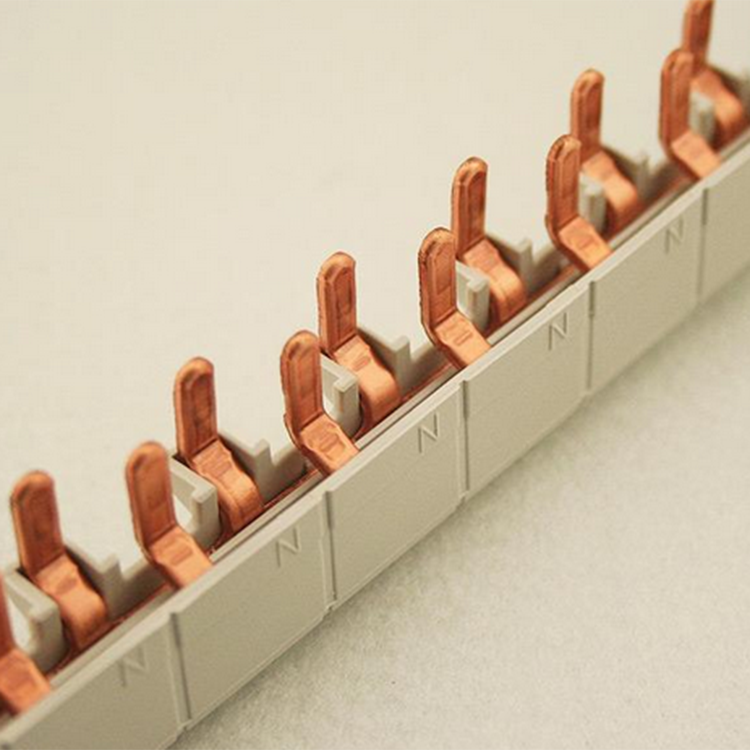
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is a Busbar Made Of?
Busbars are mostly made of aluminum or copper. Copper and aluminum are excellent materials for ensuring the effective passage of electrical energy throughout the system because of their high electrical conductivity. Copper is commonly utilized in applications needing high currents because of its strong electrical conductivity and resistance to corrosion. Aluminum is inexpensive, lightweight, and works well in many low- to medium-current applications despite being slightly less conductive.
The process of manufacturing a busbar involves several steps. First, the copper or aluminum material is cut into the desired shape and size, then machined into the desired structure through processes such as stamping, bending and drilling. To enhance its performance and durability, the surface of the busbar is often tin or nickel plated to prevent oxidation and corrosion. These treatments ensure the stability and long life of the busbar in a variety of harsh environments.
In practice, busbars are used in switchboards, substations and various industrial facilities to connect and distribute electrical energy. Their design and manufacture need to comply with strict international standards to ensure the safety and efficient operation of the system. With the development of new energy technologies, busbars are also increasingly used in areas such as solar and wind power, supporting the transmission and distribution of green energy.
Overall, the choice of materials and manufacturing processes for busbar are critical to its performance and reliability. Copper and aluminum as the main materials, through advanced processing technology, make busbar play an irreplaceable and important role in electrical distribution systems. Whether in conventional power systems or new energy sources, busbars are a key component in ensuring the efficient and safe transmission of electricity.
Different Types of Busbars
Busbars can be categorized into various types according to their materials and characteristics, which are suitable for different application scenarios and needs. Below are some common types of busbars and their characteristics:

Copper Busbar
Copper busbars are widely used in power systems for their excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance. Because copper has high conductivity, it is especially important in applications where high current transfer and low resistance are required. In addition, copper busbars have high mechanical strength and are able to withstand high mechanical stress.
Aluminum Busbar
Aluminum busbars are an alternative to copper busbars due to their light weight and low cost. Although aluminum has a slightly lower conductivity than copper, the same transmission effect can be achieved by increasing the cross-sectional area. Aluminum busbars are suitable for weight- and cost-sensitive projects such as large buildings and electrical infrastructure.
Tin Plated Busbar
Tin plated busbars are copper or aluminum busbars coated with a layer of tin to enhance their corrosion resistance and solderability. The tin plating prevents oxidization, extends the service life of the busbar, and improves contact reliability. This type of bus bar is often used in electrical equipment where high stability is required.
Silver Plated Busbar
Silver plated busbars are copper busbars plated with a layer of silver to further enhance their conductivity and corrosion resistance. The conductivity of silver is higher than that of copper, making it suitable for high-precision electronic equipment and high-frequency circuits that require extremely high conductivity and durability.
Insulated Busbar
Insulated Bus Bars cover conductive busbars with a layer of insulating material to prevent short circuits and electrocution accidents. This type of busbar is widely used in power distribution cabinets, switchgear cabinets, and other applications that require a high degree of safety. The choice of insulating material can be adjusted to suit different voltage levels and usage environments.
Flexible Busbar
Flexible bus bar is made of multi-stranded copper or aluminum wires stranded together, with good flexibility and anti-vibration performance. It is suitable for power systems that require frequent movement or vibration, such as wind turbines and mobile power stations.
Choosing the right busbar requires comprehensive consideration of factors such as current transmission requirements, cost and environmental conditions. Reasonable selection and design of busbars can not only improve the efficiency of the power system, but also ensure its long-term stable operation.
Advantages of Using Busbars
First, busbars have high electrical conductivity, which effectively reduces energy loss. This is because the large cross-sectional area of the busbar results in a lower current density, which reduces resistance. In addition, copper and aluminum, as conductive materials, have excellent electrical conductivity, which further improves transmission efficiency.
Secondly, busbars are compact and take up little space. In complex power systems, the use of busbars can simplify wiring and reduce footprint, especially important in places with limited space such as distribution cabinets and substations. Its modular design also makes installation and maintenance easier and faster.
Furthermore, the high mechanical strength of busbar can withstand large current impact and mechanical stress. This makes the busbar in the power system has a high degree of security and reliability, not easy to fail, to ensure the stable operation of the power system.
Finally, the busbar also has good heat dissipation performance. Because of its large surface area, it can effectively dissipate the heat generated during operation, prevent overheating, thus extending the service life of the equipment.
In summary, the busbar has become an indispensable and important part of the power system due to its high electrical conductivity, compact structure, high mechanical strength and good heat dissipation performance, which provides an efficient, safe and reliable solution for modern power engineering.
How Do Busbars Work?
The main function of busbars is to transfer electrical energy between equipment in the distribution system to ensure efficient power distribution. Because of their high conductivity and low resistance, busbars can transmit large currents with little loss of energy. In distribution cabinets, busbars are usually installed and secured by bolting, welding or clamping to ensure a secure electrical connection. To ensure the reliability and safety of busbar systems, factors such as load current, temperature rise, short-circuit current and mechanical strength must be considered during design. Busbar systems are commonly used in locations such as data centers, power plants, and large industrial complexes to manage and distribute power while improving system reliability and operational efficiency.
What Is a Busbar Used For?
Busbars are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Power Distribution Panels: Ensuring efficient power distribution in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
- Switchgear: Providing a reliable connection between different components in electrical switchgear.
- Substations: Facilitating power distribution and control in electrical substations.
- Data Centers: Ensuring reliable power distribution to servers and other critical equipment.
- Automotive and Transportation: Used in electric vehicles and transportation systems for efficient power distribution.
What Is a Busbar in an Electrical System?
In an electrical system, a busbar acts as a backbone for power distribution, connecting various components and ensuring a stable and efficient flow of electricity. It is a critical element in systems where reliable power distribution is essential, such as in industrial plants, commercial buildings, and infrastructure projects.
Cables vs. Busbars
In electrical engineering, cables and busbars are two common methods for conducting electricity, each with unique advantages and applications.
Cables:
- Advantages: Highly flexible, easy to install without specialized tools, suitable for various voltages (low to high).
- Drawbacks: Poor heat dissipation, prone to overheating with high currents, occupy more space in high-density wiring, complex and labor-intensive maintenance.
Busbars:
- Advantages: Excellent heat dissipation, suitable for high currents, compact design, easier fault detection and repair, ideal for high-density wiring.
- Drawbacks: Lower flexibility, unsuitable for complex wiring paths, complex and time-consuming installation requiring specialized skills and equipment, higher initial cost.
Applications:
- Cables: Ideal for flexible wiring needs and cost-effective solutions, such as residential, commercial, and general industrial uses.
- Busbars: Best for large-scale projects requiring efficient transmission and easy maintenance, such as industrial facilities and large buildings.
Table: Cables vs Busbars
| Feature | Cables | Busbars |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High | Low |
| Installation Difficulty | Simple | Complex |
| Heat Dissipation | Poor | Excellent |
| Space Occupation | Large | Small |
| Maintenance Difficulty | High | Low |
| Initial Cost | Low | High |
| Voltage Range | Low to high voltage | Mainly medium to high voltage |
| Suitable Applications | Residential, commercial, industrial | Industrial, large buildings |
FAQs on Busbars
Q: What is the typical voltage rating for busbars?
A: Voltage ratings for busbars vary widely depending on the application and design. They can handle voltages from low–voltage systems to high–voltage applications.
Q: What are the benefits of using a busbar over traditional wiring?
A: Busbars provide higher efficiency, space savings, flexibility, safety, and ease of installation.
Q: How are busbars used in renewable energy systems?
A: Busbars are essential components in solar and wind energy systems for collecting and distributing the generated electricity. They provide a reliable and efficient path for current flow between the power source and the grid or load.
Q: Can busbars be customized?
A: Yes, busbars can be customized to meet specific application requirements, offering tailored solutions for different industries.
Q: What is a busbar trunking system?
A: A busbar trunking system is a prefabricated modular system that consists of busbars enclosed in a protective housing. It provides a flexible and easily expandable power distribution solution.
Want To Learn More? Click Here To View Product Details!
--- END ---
INFORMATION
PRODUCT
- Busbar Support
For the bus bar frame option, first confirm the specification of your own copper bar. After confirmation, confirm how many phases your bus bar frame is, how many copper bars in total, and what is the phase to phase distance between each phase copper bar and another phase copper bar. Select the type according to the size you need. The common spacing is 55, 80, 100, 110, 120, 130, 140, 150, 160, 175 and 180 (unit: mm). The number of phases includes single phase, three-phase, four phase and five phase. The copper bars that can be installed in each phase are divided into single row, double row, three row and four row.There is also the size of the mounting screw hole of the busbar clamp.
- Heat Shrink Tube
Heat shrink tubing is a tubular heat-sensitive plastic sleeve that shrinks in diameter when heated. It is used to insulate and protect cables, wires and hoses. Heat shrink tubing can also be used as a covering for cable connectors. When heated, the tube shrinks tightly around the connector, creating a waterproof and corrosion-resistant seal. Heat shrink tubing provides electrical insulation, mechanical protection, environmental sealing and strain relief. Our heat shrink tubing offers single and double wall tubing designed for a variety of applications including back end connector sealing, breakout and connector-to-cable transitions. It is a reliable alternative to tape, molding or potting. In addition, our shrink tubing is made of high-quality materials that provide superior protection and insulation. We offer a variety of sizes and colors so you can find the perfect heat shrink tubing for your needs.
- High Voltage Insulator
High-voltage insulators are essential components in high-voltage applications. It is designed to protect people and equipment from high voltage electricity. For electrical building maintenance, power plants, substations and other places that require insulation. An electrical insulator is a material that hinders the free flow of electrons. Providing reliability, availability and power density is critical for all modern electrical energy and power systems.
- Low Voltage Insulator
Low voltage insulators are an essential part of any electrical system. It provides the reliable and efficient insulation needed to protect electrical equipment and circuits. It is used to protect people and equipment from injury or damage due to short circuits or overloads in electrical systems. Low-voltage insulators are made of high-quality materials and are durable. Haitan offers a full line of low voltage brackets, cost-effective insulators with extremely high electrical and mechanical parameter stability and very high leakage current resistance.
BUSBAR CLAMP
- MD Busbar Support
MD bus support busbar frame insulator is made of BMC / SMC, which is used to support the bus circuit system in the same equipment and to support single-phase, three-phase, four phase and five phase buses. It is used for low-voltage distribution lines and communication lines, and is widely used in electrical applications such as distribution box, switchgear, inverter and green power supply.
- EL Busbar Support
Marble busbar clamp, foreign trade type
- A Series Busbar Support
White busbar clamp, small size, convenient storage and flexible combination
LOW VOLTAGE INSULATOR
- SM Insulator
Reinforced insulator can be applied to higher strength electrical use
- MNS Insulator
High strength insulator, with higher strength and larger insert, can improve greater support
- SB Insulator
New energy insulator is suitable for high-strength service environment such as electric vehicle and charging pile, with strong stability and smaller volume
- EN Insulator
- CY Insulator
- DY Insulator
- SE Insulator
- MG Insulator
- PT Insulator
Ordinary insulator, suitable for ordinary wire connection
- CT Insulator
 E-mail: [email protected]
E-mail: [email protected]
 No. 20 Lingyun Road, Dongfeng
No. 20 Lingyun Road, Dongfeng
Industrial Zone, Liushi Town, Yueqing
City,Zhejiang Province


© Copyright 2024 China Haitan Electromechanical Technology Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.SUPPORT BY:JUNJ Privacy Policy
