Power Distribution Block: Everything You Need to Know
1. Introduction
In modern electrical systems, especially within control panels, automation lines, and energy management networks, power needs to be delivered safely and efficiently across multiple circuits. This is where the Power Distribution Block (PDB) comes into play. Whether you are designing an industrial control cabinet or sourcing components for renewable energy infrastructure, understanding how a PDB functions will help you make better, more compliant design and purchasing decisions.
This guide breaks down the essentials of power distribution blocks: from how they work, what they’re made of, to where they’re used, and how to choose the right one. Think of it like a power splitter for circuits—only far more robust and compliant with modern electrical safety standards.
2. What is a Power Distribution Block?
2.1 Definition
A Power Distribution Block is an electrical component that splits a single input power feed into multiple output circuits. It acts as a centralized junction point, allowing a high-current source to safely and efficiently supply several downstream loads.
Also referred to as an Electric Power Distribution Block, Power Terminal Block, or Power Distribution Unit (PDU), it is commonly used in low voltage systems, automation equipment, energy storage solutions, and solar PV setups. This type of electrical connector streamlines your electrical wiring accessories into an organized, scalable distribution system.
2.2 Construction & Materials of Power Distribution Block
A standard PDB is composed of the following:
- Conductive Busbar/Core: Typically made from high-conductivity copper or tin-plated aluminum. This part handles the current transfer.
- Insulated Housing: Built with flame-retardant thermoplastic materials (e.g., polycarbonate or PC+ABS) and rated to UL 94-V0 for fire safety.
- Mounting Base: Designed for compatibility with DIN Rail Power Distribution Block systems or screw-fixed onto panels.
- Terminal Ports: Screw or clamp terminals that accept both solid and stranded conductors. Transparent covers are often included for safety and inspection.
Advanced models may include features like:
- Touch-safe protection (IP20/IP30 and above)
- Transparent inspection windows
- Pre-installed surge protection devices (SPD)
- Communication modules (RS485, CAN) for smart power management and monitoring
2.3 Key Functions of Power Distribution Block
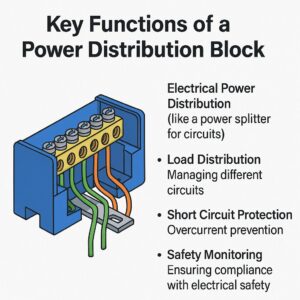
- Power Splitting: Enables branching of main power input into multiple sub-circuits.
- Load Management: Helps balance and distribute current across various loads, ensuring load balancing and system efficiency.
- Space Optimization: Reduces wiring complexity and improves internal cabinet layout.
- Safety Assurance: Provides short circuit protection, thermal resistance, and overvoltage defense when integrated with fuses or circuit breakers.
2.4 Benefits of Power Distribution Block
- Modular Design: Easily expandable or configurable for future needs
- Reduced Labour Costs: Simplifies installation and shortens wiring time
- Reliability: Low-resistance connections ensure stable voltage and power supply
- Versatility: Compatible with multiple conductor types, suitable for both copper and aluminum
- Durability: Resistant to vibration, temperature changes, and environmental stresses
- Compliant Performance: Meets electrical safety standards and ensures secure current routing
3. Application of Power Distribution Block
Power Distribution Blocks are versatile industrial electrical components used across various industries:
| Industry | Application Example |
| Industrial Automation | Power branching to PLCs, relays, drives |
| Data Centres | Clean power distribution in server racks |
| Renewable Energy | Solar combiner boxes, EV charging stations |
| Commercial Buildings | Load distribution in HVAC and lighting panels |
| OEM Machinery | Distribution from main circuit to control logic and drives |
| Telecom | Cabinet-level voltage branching in base stations |
Their modularity makes them ideal for use in DIN rail junction boxes, panel boards, and smart metering enclosures. They contribute significantly to centralized load distribution and simplified electrical wiring accessories planning.
4. How to Choose the Right Power Distribution Block
When selecting a PDB, you need to evaluate both technical specifications and application environment:
- Rated Current: Common ranges include 125A, 250A, 400A, and 600A. Choose according to your total load demand.
- Voltage Rating: Ensure compatibility with your system voltage (typically 600V or 1000V for industrial systems).
- Conductor Size & Type: Match with the wire gauge (e.g., 1/0 AWG in, 6x 10 AWG out) and material (copper/aluminum).
- Mounting Method: Opt for DIN Rail Power Distribution Block if modular installation is preferred, or screw-mount for fixed setups.
- Poles / Circuits: Consider how many output circuits you need (single-pole, double-pole, or three-phase).
- Certifications: Look for UL 1059, IEC 60947-7-1, CE, RoHS compliance.
- Environmental Rating: For enclosed or outdoor use, choose models with IP65 or higher protection.
- Extra Features: Need smart monitoring? Look for models with RS485 or CAN interfaces.
5. Conclusion
A Power Distribution Block is not just a passive terminal block—it’s a vital node in your electrical power distribution plan. It improves system safety, simplifies wiring, and ensures reliable power delivery in everything from factory floors to solar arrays.
Whether you need a compact din rail junction box, a high-capacity power terminal block, or a modular power solution for your next project, choosing the right PDB ensures compliance, efficiency, and scalability.
Need help sourcing or configuring your ideal power distribution setup? Reach out to our team of electrical experts for custom solutions that meet UL, IEC, and industry-specific standards.
--- END ---
Prev: Electrical Safety Made Easy with Wall Mount Ground Bar
Already the latest article
© Copyright 2024 China Haitan Electromechanical Technology Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.SUPPORT BY:JUNJ Privacy Policy


 E-mail:
E-mail:  No. 20 Lingyun Road, Dongfeng
No. 20 Lingyun Road, Dongfeng 
