Busbar Insulator: A Complete Guide
What Is Busbar Insulator?
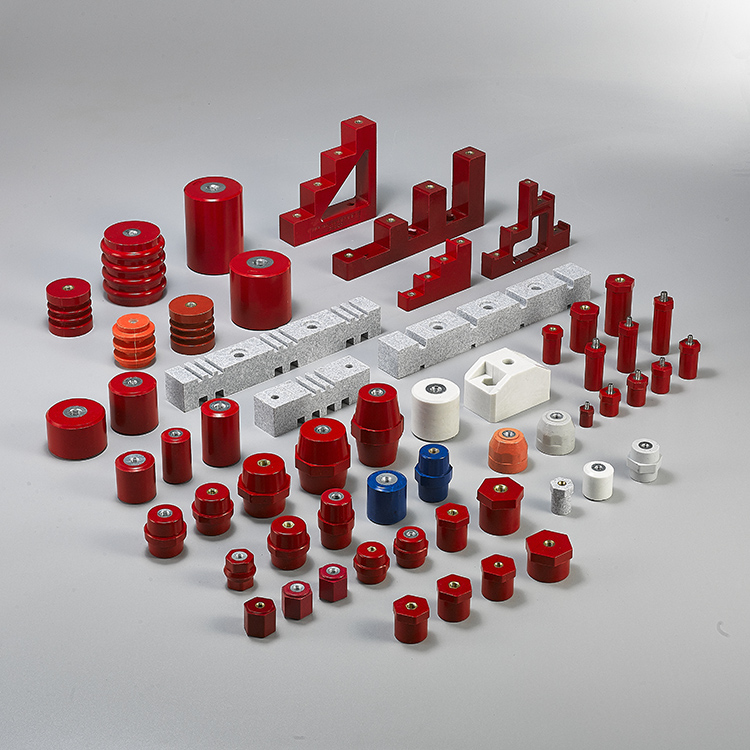
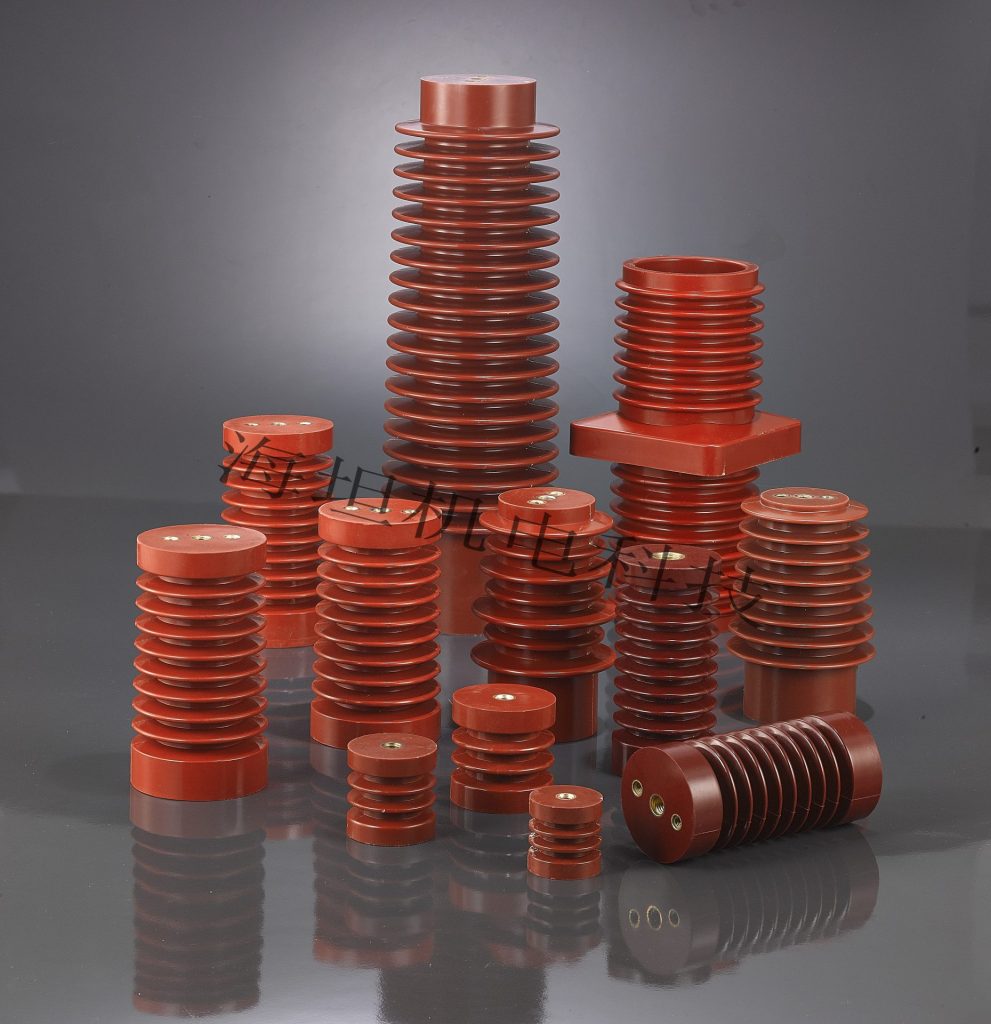
Busbar Insulator is a type of insulating device that is used with busbars. Busbars are conductive strips or bars made of materials like copper or aluminum that carry electricity in switchgear, panel boards, and busway enclosures. The main purpose of the insulator is to create electrical separation between the busbar and its surrounding enclosure or other conductive parts, which helps prevent accidental contact and potential short circuits.
Types of Busbar Insulator

Busbar insulators vary in shape and size depending on the specific application and voltage requirements. Common types include:
– Standoff Insulators: they are usually cylindrical or conical in shape and ensure consistent spacing between the busbar and the mounting surface to provide proper air insulation and prevent accidental contact.
– Support Insulators: they are used to support and hold the busbar in place within the enclosure. These insulators may have slots or clamps to facilitate installation.
– Strain Insulators: Used in the presence of mechanical stress or vibration to provide additional support and prevent movement of the busbar due to external forces.
Why is Busbar Insulator Important?
The importance of busbar insulation cannot be ignored. It plays a vital role in the following areas:
– Preventing Short Circuits: Busbar insulator effectively prevents accidental contact between busbars and other conductive parts, thereby reducing the risk of short circuits and improving the safety of personnel and equipment.
– Increasing Efficiency: The use of appropriate insulating materials reduces energy losses due to leakage currents, which in turn improves the efficiency of the distribution system and reduces operating costs.
– Boosting System Reliability: The application of busbar insulators not only prevents insulation breakdown but also ensures the continuous operation of the system, thus greatly improving the overall reliability of the electrical system.
Materials of Busbar Insulator
Busbar insulators are usually crafted from materials that possess superior dielectric properties and strong mechanical capabilities. Some common materials used include:
– Epoxy Resin: This type of thermosetting polymer provides top-notch electrical insulation, mechanical strength, and can withstand environmental elements such as moisture and heat.
– Bulk Molding Compound (BMC): A composite material made up of a thermosetting resin reinforced with glass fibers, offering exceptional electrical and mechanical characteristics.
– Ceramic: Traditional ceramic materials like porcelain offer high dielectric strength and resistance to high temperatures, although they may be more fragile compared to polymer-based insulators.
FAQs on Busbar Insulator
Q: What factors influence the choice of busbar insulator?
A: Several factors determine the suitable insulator type, including voltage level, current rating, environmental conditions, space constraints, and desired level of mechanical support.
Q: How are busbar insulators installed?
A: Installation methods vary depending on the insulator type and application. They may be bolted, clamped, or glued to the mounting surface.
Q: How often should busbar insulators be inspected?
A: Regular inspections are crucial to ensure the integrity of the insulators. Inspection frequency depends on factors like environmental conditions and system criticality.
Q: Can busbar insulators be repaired or refurbished?
A: In some cases, minor damage to insulators may be repairable. However, it’s often recommended to replace damaged insulators to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Want To Explore More Quality Products?
CJ Series, CT Series, CY Series, DY Series, EL Series, EN Series, MG Series, MNS Series, PT Series, SB Series, SE Series, SM Series
--- END ---
© Copyright 2024 China Haitan Electromechanical Technology Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.SUPPORT BY:JUNJ Privacy Policy

 E-mail:
E-mail:  No. 20 Lingyun Road, Dongfeng
No. 20 Lingyun Road, Dongfeng 
